- 06 April 2021
- Announcements
- 24 Comments
Smart Contracts Explained: An Introduction for Beginners

The blockchain has many enticing benefits, but perhaps chief among them is its decentralised nature. The decentralised aspect is shared between all parties associated with the network, meaning that involvement of third-parties and unwanted intermediaries is negated. Out of many alluring features, this is perhaps the most attractive, minimising the chances of conflict with processes and generally saving time. Admittedly, blockchain technology has problems that have yet to be fully resolved, but it does present an altogether more efficient and cost-effective alternative to more conventional systems.
The genesis of the Smart Contract concept
Out of all the various applications presented by blockchain technology, smart contracts are among the most useful and commonly utilised. Smart contracts as a concept are nothing new. The notion of them was first introduced back in 1994 by cryptographer Nick Szabo, who drew the conclusion that a decentralised ledger can be utilised as contracts that are self-executable. This concept was later termed as Smart Contracts, with said digital contracts able to be concerted into code form, thus allowing them to be run on a blockchain.
As an idea, smart contracts are nothing new. However, a paper-based contract infrastructure remains the norm. Even when used in a widespread context, digital contracts rely on the involvement of trusted third-parties in order to be fully executed. This approach might have proven functional to a point, but the fact is, allowing for third-party involvement invites all manner of security risks and the increased chance of fraud activity. It also affects the overall cost of any given transaction.
As we enter into an era where the blockchain is being properly utilised, these issues can be resolved. One of the hallmarks of a system based on the blockchain is that all entities within that network interact in a distributed way, thus removing the need for a trusted third-party to be involved. Simply put, blockchain technology allows for data storage on a distributed ledger. This information, stored data regarding transactions and records, is available in real-time to all entities in the network.
Blockchain technology first entered into the public consciousness with the emergence of cryptocurrency, namely Bitcoin. However, beyond its cryptographic applications, blockchain technology has developed radically and its applications for various industries are now becoming more apparent.
In particular, smart contracts stand as one of the most effective areas of application that blockchain technology presents. The reasons for this are numerous. One such benefit is that smart contracts minimise transaction costs when compared to usage of conventional contracts. Nowadays, more customised and tailored smart contracts are possible thanks to innovative functions like Turing-completedness, a feature boasted by leading blockchain platform, Ethereum. With these innovations mind, smart contracts can be successfully applied to all manner of distinct industries.
An introduction to Smart Contracts
Simply put, a smart contract is computer code shared between two or more individual parties. This set of code runs atop a blockchain base, with rule sets determined by all involved parties. When said code is executed, the smart contract will execute itself and achieve output if all rule definitions are met and adhered to. Decentralised automation is made allowable by this code, with the conditions agreed upon facilitated, verified and enforced. Smart contracts can be used to exchange value assets such as shares, property, currency and more with a high level of transparency. This keeps things free of conflict and removes the requirement for an intermediary middleman.
You only need consider a real-world process in order to see the benefits of smart contracts. Consider for example, a situation where you might require a court-registered document. To begin with, you’d need to approach a legal representative and part with money to secure their services. There would then a be a waiting period before you have access to the required document. This process can be made all the more efficient when you use smart contracts. The sought-after document is yours simply by paying for it and it alone. You wouldn’t have to consider the involvement of a third party, let alone fork out for their services. Furthermore, in the case of smart contracts, things aren’t limited to rule definition surrounding an agreement. Rather, they’re also responsible for the automated and automatic execution of associated obligations and rules.
Smart contracts, in their easiest to understand form, can be seen as programs that operate in accordance to the format outlined by those who’ve created them. They’re perhaps most useful in business, when business collaboration requires associated parties to agree upon outlined terms and conditions. This utilisation of smart contracts not only drastically slashes the chance of fraud, it means that there is no need for involvement from third-party intermediaries. What’s more, costs can be significantly reduced.
In most cases, smart contracts operate on a process where digital assets and several parties are involved, specifically where said parties require automatic control over their assets. Assets can be deposited and redistributed easily among participants, within the outlined rules of the contract that is. The perks and benefits of smart contracts are numerous, with some of the most attractive being the ability to monitor and track performance in real-time, while also greatly minimising costs. In summary, chief features of successful smart contracts include being self-executable and self-verifiable, while also standing as tamper-proof alternatives to traditional contracts.
Understanding how Smart Contracts work
To get a better understanding of how smart contracts work, it’s worth considering an example with real world relevance. Here, we’ll look at the property market. Consider the hurdles and implications of selling property. Stacks of paperwork and ongoing dialogue with various parties are both hallmarks of selling property, while risk factors like fraud are also essential considerations. Currently, most individuals who dare to deal in property don’t enter into proceedings as a solo endeavour. Rather, they venture into deals with the help of a real-estate agent. Market considerations and paperwork are usually concerns then left to the agent to deal with. In short, they serve as intermediaries in the process, maintaining chief oversight over the deal itself and handling any major negotiations.
In this example, the role of the middleman, in this case the real-estate agent, is to overcome the inherent risk associated with the transaction. Said agencies provide the facility of escrow services, which allow for funds to be transferred from Party A to Party B. Once a deal is reached and made final, Party A will have to pay both the agent for their services and any commission, as well as cover the costs of the escrow service provided. The end result is added cost to the buyer, as well as an increased chance of risk for the seller.
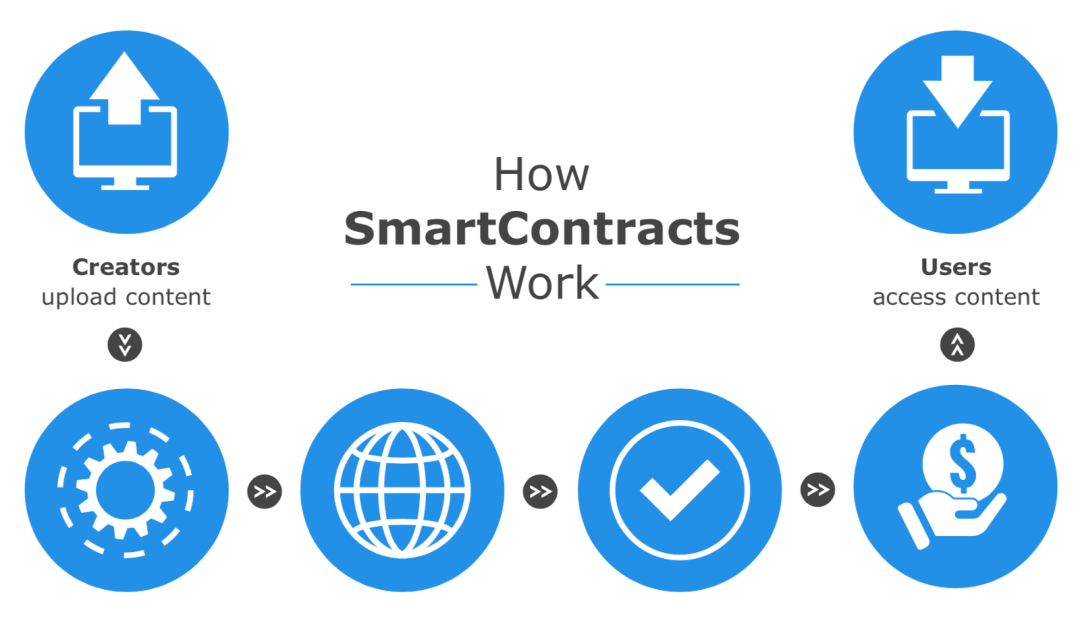
How can smart contracts better serve both parties in this instance? For a start, the whole process can be rendered more effective by minimising burden to all. Smart contracts are by definition designed to function on a principle based on conditions. This serves to overcome inherent ownership issues, with the transfer only happening when financial conditions and other requirements are finally agreed upon. Furthermore, smart contracts can make additional elements like escrow services redundant, completely replacing them in the process.
A distributed system can be used to store both the right of possession of a given property as well as associated monies. These can be viewed by all involved parties at any instance in real-time. When it comes to the final transfer of money, the transfer can be viewed by all participants of the network, completely eradicating any risk of fraud. Furthermore, such levels of transparency eliminate any trust issues, completely negating the need for an intermediary. A real-estate agent and their chief functions can be wholly replaced by code implemented into the smart contract. The entire process is made all the more efficient, saving both time and money for both buyer and seller. It’s truly a win-win situation.
The key benefits of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts have the potential to dramatically improve everyday life and are a clearly advantageous alternative to conventional contracts. They are inherently faster and more convenient for all involved, dramatically streamlining workflows and boosting operational efficiency. What’s more, smart contracts are incredibly user-friendly and simply implemented, while delivering peace of mind and reassurance when it comes to security. Perhaps most advantageous to everyday applications however, is how smart contracts do away with the need for intermediaries.
As blockchain technology continues to evolve and advance, we’re likely to see a massive uptake in the application of smart contracts. Need more convincing? Below, we’ve outlined further benefits that make smart contract usage a no-brainer.
1. Utmost transparency
When it comes to discussing the benefits of blockchain and smart contracts, transparency is key. In the case of smart contracts, terms and conditions are outlined in meticulous detail that can be assessed by all involved parties. The obvious benefit here is that such transparency negates the likelihood of there being disputes down the line, with terms and conditions only being finalised and approved after all involved participants have agreed to them. Furthermore, the requirement for the utmost in precision means that all information is kept open and accessible to all, eliminating miscommunication errors and issues. In short, the transparency that smart contracts bridges communication gaps and ensures everyone is well and truly on the same page at all times.
2. A more efficient way to do business
If time is money, then smart contracts are a sure-fire time-saving initiative. Almost anything involving the processing of documents takes time, with that timespan taking days as a minimum. The reasons for slothful processing are numerous, but unnecessary extra steps and the involvement of multiple intermediaries are major contributors. When smart contracts are utilised, a great deal of time is saved all round due to the process being largely automated. What’s more, by removing manual processes from the equation, unexpected and unnecessary delays are eliminated, saving even more time down the line.
3. Superior standards in safety and security
The automated coding benefits of smart contracts make them a go-to choice in an era of data encrypted technology. As smart contracts adhere to the strictest standards in safety and security, they offer incredible levels of protection that makes them desirable in circumstances where critical processes need to be considered.
4. Increased confidence and trust
The transparent nature of smart contracts combined with their impressive security credentials make them a reliable option for use in business. The aforementioned features eliminate the chance of manual error and manipulation, ensuring incredibly high levels of confidence in their ultimate execution. Once all terms and conditions have been agreed upon by involved parties, a smart contract is automatically execute, without requiring manual input. The self-executing nature of smart contracts also negates litigation and legal concerns for involved parties.
5. Accuracy and precision
By definition, smart contracts are incredibly detailed in nature. A perquisite for smart contracts is that all terms and conditions need to be included before they can be deployed. The absence of a required condition might result in an error in equation, but smart contracts always include required conditions in detail. Once created and completed, a smart contract forms a comprehensive final agreement which more or less completes the process once executed. Compare this to manually created contracts which have the potential for a high margin of error. The person drafting an agreement might forget to include important terms and conditions, while it’s impossible to track the creation process for incidences of errors until any error is made. All in all, smart contracts are a much more attractive prospect for those looking for top-tier levels of accuracy.
6. Desirable data storage features
The data storage capabilities of smart contracts are very desirable to involved parties. They are entirely accurate, maintaining a precise record of an agreement down to the tiniest metric. All possible details associated with a transaction are reliably stored on said smart contract, while anyone involved in the transaction has the option to access this information at any time. What’s more, these transactions are then stored on the blockchain. These future records are an indispensable reference in the unlikely event of a dispute arising later down the line.
7. Considerable cost savings
With businesses across all industries looking to slash costs, a move to smart contract implementation is a clear win. For a start, smart contracts require the involvement of only those who form part of said agreement. There’s zero need for intermediaries and middlemen to be involved in the process, instantly eradicating the associated cost of them. Furthermore, all of those additional process steps associated with paper-based contract documents are done away with, as are the costs attributed to them.
8. An eco-friendly alternative
This might seem small fry in the grander scheme of things, but a move to paperless processes shouldn’t be ignored in its importance. Smart contracts are wholly computer coded, meaning that paper isn’t required at any step. Not only does this reduce basic costs for businesses, it also serves to make companies more environmentally-friendly in their everyday operations.
Exploring the benefits of Smart Contract applications
Whether it’s the simple act of purchasing a product or committing to a new job role, contract agreements are a prerequisite, serving as proof of agreement in such instances. Historically however, traditional processing of paperwork and paper contracts has incurred significant costs, involvement of third parties and an increased chance of error.
As we move more fully into a digitised world and technology develops accordingly, we can look forward to a reality where these everyday processes are made all the more reliable, efficient and cost-effective. How? With the implementation of smart contracts. By their very nature, smart contracts as a concept are designed to remove the need for middlemen and unnecessary third-party input, making the overall systems in place more efficient. When it comes to considering their widespread application, smart contracts can be applied to a wide variety of industry sectors. Below, we’ll explore a few of these sectors and how smart contracts can benefit them.
1. Streamlining claim processing in the insurance sector
This is one sector that can enjoy big benefits from smart contract application. Currently, an overall lack of automation in administration, particularly when it comes to claim processing, means insurance companies face lengthy processes that can total months in average duration. This not only causes an issue for insurance companies, but also has a direct effect on the customer. Furthermore, these lengthier processes incur higher overall administrative costs, with the potential for inefficiency high and a significant chance of the end result being an unhappy customer.
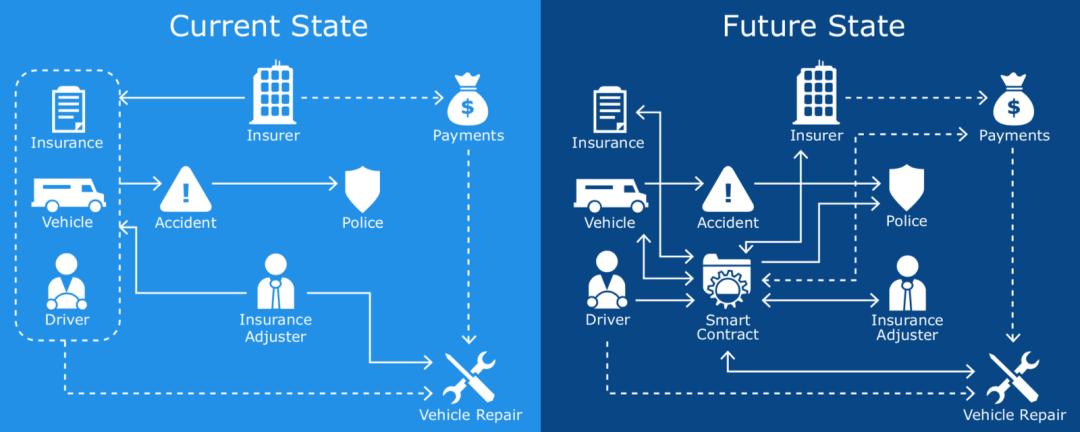
Claim processing application in the insurance sector Smart contracts can revolutionise the way business is carried out in the insurance sector, simplifying things and streamlining processes significantly. Case in point, if applied correctly, smart contracts could ensure payment requests for claims are triggered automatically once required conditions are met. What’s more, when it comes to time-sensitive cases where legitimate claimants have a very urgent need for payout, unnecessary waiting times are all but eliminated.
2. Enhanced trust and transparency with employment contracts
This is one area where the application of smart contracts will be very welcome. Ordinarily, in the event that either an employer or employee doesn’t meet with the agreed upon expectations, the terms of the agreement itself can be compromised. This issue is entirely negated by the use of smart contracts. Simply by implementing a single smart contract for both the employer and employee, terms and conditions are made crystal clear and establish a high degree of trust and fairness. Associated records can relate to all manner of factors, be it key responsibilities and role remit, salary amount and bonus implications and more. Should any conflict between parties arise, these records can be quickly accessed to reach a resolution. The end result is a far better relationship between employer and employee.
Smart contracts have broader applications in the workplace. When it comes to processing wages, smart contracts can be implemented to ensure an employee receives the amount agreed upon in their contract in accordance with time periods outlined in terms of said contract. Furthermore, the transparent nature of smart contracts is particularly useful when temporary contractors are used to meet business needs, especially when outside agencies are involved. In particular, third-party agencies cannot interfere with contract terms once an individual is hired by a company, with any changes made to terms instantly detectable when smart contracts are utilised.
3. Simplifying supply chain management
In simple terms, effective supply chain management refers to the movement of goods from the very initial stage to the final stage of a chain. Supply chain management is a key component of many industry sectors, with successful supply chain operation of paramount importance to businesses. Such a crucial function can’t rely solely on one person, with many distinct contributors needing to be involved. Smart contracts can bring new levels of efficiency and essential assurances to the supply chain process. As goods move through the chain, ownership rights can be properly recorded, with all individuals within the network able to monitor and track the precise location of any given product at any time.
These checks can be carried out throughout the process, up until said goods arrive with the end recipient or customer. Should an item end up missing, smart contracts can be effectively utilised to quickly identify its location. What’s more, should any stakeholder involved fail to honour contractual obligations as laid out in contract terms, the inherent transparency of smart contracts means that all other parties can observe this. This level of transparency is particularly desirable in the context of supply chain systems.
In a general sense, smart contracts boast many advantages that can benefit a wide cross-section of industry sectors. In addition to providing high levels of transparency, they make processes more efficient and save time, while also reducing unnecessary overhead costs. They’re certainly a more reliable and secure alternative to conventional paper contract documents, but to ensure these standards are upheld along with higher levels of efficiency and trustworthiness, it’s essential care be taken when implementing them. Risk awareness of implementing smart contracts is crucial for any business looking to adopt them, while great care needs to be applied to minimise the chance of code corruption which can derail smart contract application efforts.
In summary
The potential applications of smart contracts are plentiful. Not only can they be utilised in regards to everyday agreements, they can be turned to when forming contracts between business enterprises and state institutions. The transparent nature of them and levels of trust they foster make for a much fairer landscape where everyone can enjoy higher levels of confidence in processes.
Furthermore, the age of the middleman will soon be brought to an end thanks to smart contract implementation. Costly fees charged by intermediaries needn’t be a concern thanks to the application of smart contracts, which wholly replace the function of these third-party entities. In fact, the only base concern to consider when using smart contracts is that code be checked before ultimate execution. Once that’s been cleared, everything else is then automated. The end result is a streamlined process that’s fully automated, whether it’s an everyday transaction or something more substantial.
As technology continues to evolve, smart contracts will likewise need to be developed and maintained to ensure no issues in compatibility so they can continue to perform properly. The era of smart contracts is also still in its infancy, meaning that smart contracts might still be vulnerable to attacks. To ensure that smart contracts can bring their many benefits to our everyday existence, general cybersecurity measures will need to be updated systemically, as will the creation platforms used to generate smart contracts going forward.